To be certain we have a secure system from chip to cloud, it is fundamental to boot device from a trusted BIOS - often referred as secure boot. HP Connect for Microsoft Endpoint Manager is a cloud application designed to ease the management of UEFI BIOS on supported HP systems. This blog post will cover updating the BIOS on HP devices using MEM.
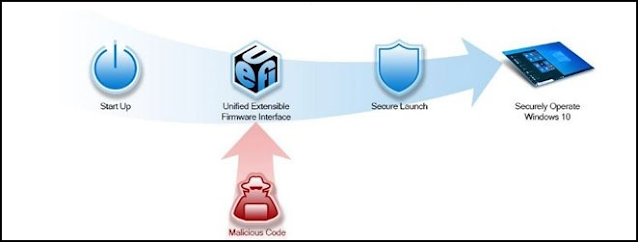 |
| We need to have control of the boot environment of our managed devices |
Please note: This is not a sponsored post!HP Connect for MEM
HP Connect for MEM has a framework to develop BIOS management policies that are published to Microsoft Endpoint Manager device groups. While HP Connect creates the policies, Microsoft Endpoint Manager (Intune) executes them as compliance proactive remediations. No additional software is required to be downloaded or installed in each device.
HP Connect for Microsoft Endpoint Manager supports the following policy features:
- BIOS Updates
- Always up to date
- Critical versions only
- specific version
- BIOS Settings
- Supported on a per platform basis
- BIOS Authentication
- HP Sure Admin (HP Sure Admin Infosheet)
- Passwords
The requirements for using HP Connect for Microsoft Enpoint Manager are:
- Administrative access to Microsoft Azure
- An appropriate subscription for Microsoft Endpoint Manager which allows the use of Proactive Remediations
HP Connect is a cloud application free of use, and it interacts directly with an Azure Active Directory tenant to access device groups and to publish BIOS policies to these groups.
Onboarding to HP Connect
- Log in to https://admin.hp.com as a Global Administrator for the tenant.
- Accept the permissions for the organization.
After this initial process, an Intune Administrator will be able to login and use HP Connect for the organization.
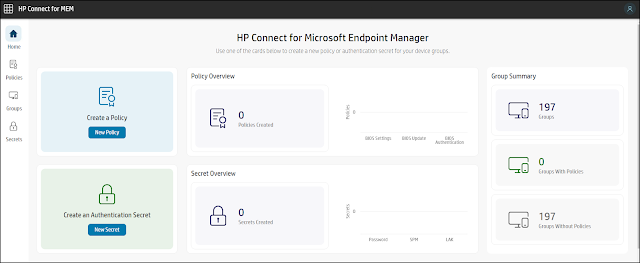 |
| The Home page for HP Connect for Microsoft Endpoint Manager |
Groups
Under the Groups menu on the left hand menu, you will find security groups imported from Azure Active Directory (AAD). We will create a dynamic device security group in AAD containing all HP devices for this demo.
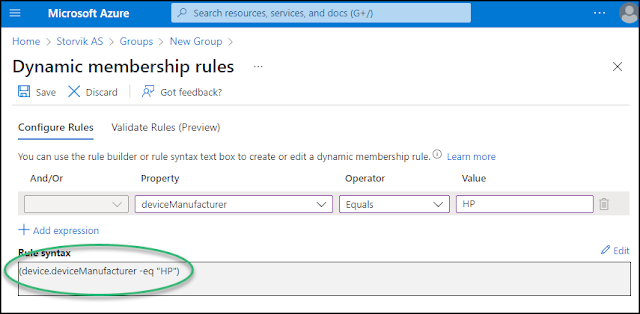 |
| (device.deviceManufacturer -eq "HP") |
The values can be queried directly on the devices if you want to verify the accuracy:
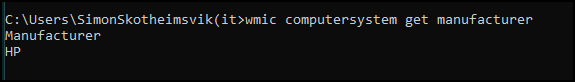 |
| wmic computersystem get manufacturer |
After a while, the security group will be populated with devices, and a refresh in the HP Connect portal will reveal the group.
HP Connect Policies
This blog post will concentrate on making sure all Bioses are up to date. I will not address policies applying settings or controlling authentication in the BIOS this time.
Bios Update Policies
There are 3 types of BIOS update policies supported by HP Connect:
- Keep BIOS of all devices always updated
- Deploy only critical BIOS updates
- Establish a rule for a specific device model
Policy to keep all devices always updated
This time I will create a policy when applied to a group of supported devices, Microsoft Endpoint Manager (MEM) will use the policy as a compliance item to monitor and update every device in the selected group every time a BIOS is released that matches a device.
- Navigate to Policies in the left hand menu of HP Connect for MEM and create a new policy
- Define a Policy Name which will be shown in MEM. Set the policy type to be Bios Update
- As BIOS update method, select to "Keep BIOS of all devices always updated".
- The new policy will now be created, and it can be applied to Azure AD Groups and published to AAD.
The new proactive remediation policy is now published to MEM.
How is the policy applied?
When the policy is added to Microsoft Endpoint Manager, Intune will use its native Windows 10/11 agent to send the policy action to all devices in the collection at scheduled times. By default, the policy is checked and applied every 60 minutes. This schedule can be modified to run once, every hour or at a daily basis.
The Intune agent send a task to each device assigned the policy as an action to be performed. THP HP action queries the HP cloud for BIOS versions newer than the installed one on the device. If a newer one exists, the signed version is downloaded and applied to the device. This will follow these steps:
- BIOS UEFI capsule bin file is downloaded
- The capsule file components are hosted on the UEFI System partition
- UEFI BIOS in device is made aware of the pending update
- On next reboot, UEFI BIOS performs the update
A BIOS
update policy will not automatically restart the device: therefore, the update
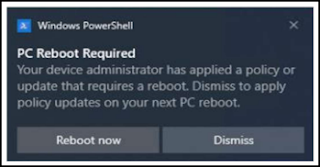
will not occur until such action is taken. Once a BIOS update policy is
applied, the device will display a toaster notification message like the
following:
The BIOS update will occur once the device is rebooted.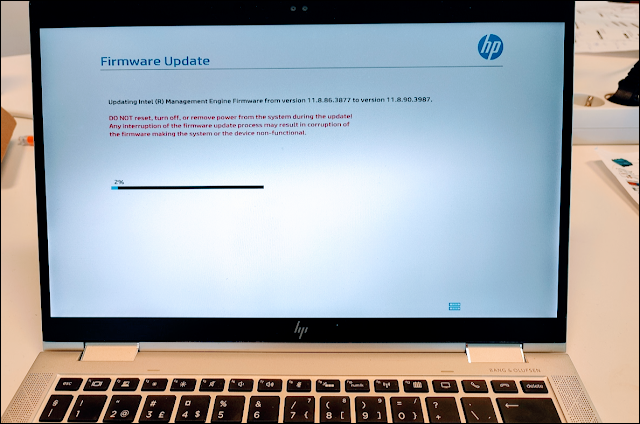
The overview for the configured proactive remediation gives information about how the script package is performing on the targeted devices.
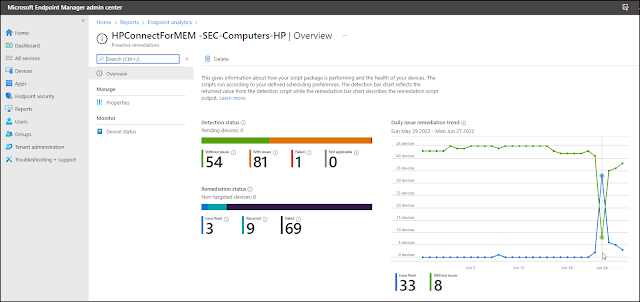 |
| Note the change in the graphs as a new BIOS version is available and updated |
Bitlocker recovery key?
Please be aware that some devices will require the user to enter the Bitlocker Recovery Key after BIOS and Firmware upgrades.
Windows will require a recovery key for Bitlocker when it detects a possible unauthorized attempt to access data. This can also happen on changes in hardware, firmware or software which Bitlocker finds suspicious and can't distinguish from a possible attack. The end user can in such settings often find the Bitlocker recovery keys for it's own devices on the device-list in My Account (microsoft.com). If not, please refer to the article
Finding your BitLocker recovery key in Windows (microsoft.com) 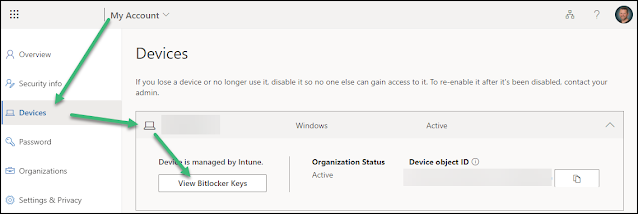 |
| A Bitlocker recovery key can be found in My Account if integrated with Microsoft Azure AD |
Next step: Bios Authentication Policies
BIOS Authentication is an important aspect of managing, controlling, and securing Windows devices. The BIOS contains the start-up code for the hardware, including settings that should be secured prior to booting into Windows. If the BIOS can be accessed without authentication, a local or remote user may be able to disable basic security features, or introduce malware early into the startup process that Windows may not protect against.
Now as the BIOS versions are up to date with the newest security and vulnerability updates, the next step should include getting control over the BIOS authentication. That will be the topic of a follow-up blog post.


















No comments:
Post a Comment